- Platform
- About us
- Resources
- Events
Whitespace Health is SOC2+ Certified
SOC2+ is an AICPA Combined Certification
AICPA (American Institute of Certified Public Accountants) packaged the requirements of SOC2, HITRUST, ISO-27001 and NIST to create the SOC2+ designation. SOC2+ certification is achived after successful completion of an audit by an independent licensed CPA for all of these elements. SOC2+ compliance is considered the goal standard for SaaS providers.

View the SOC2+ data sheet
Data Sheet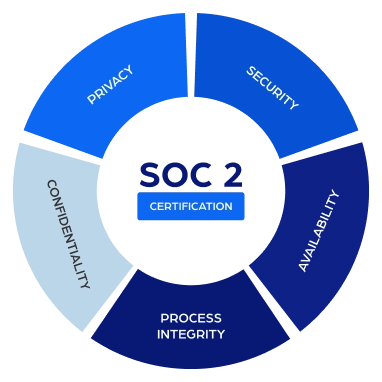
5 Elements of Trust Services Criteria
-
Security
-
Availability
-
Process Integrity
-
Confidentiality
-
Privacy
The security principle refers to protection of system resources against unauthorized access. Access controls help prevent potential system abuse, theft or unauthorized removal of data, misuse of software and improper alteration or disclosure of information. IT security tools such as network and web application firewalls or WAFs, two factor authentication and intrusion detection are useful in preventing security breaches that can lead to unauthorized access of systems and data.
The principle of availability refers to the accessibility of the system, its products, or services, as stipulated by a contract or service level agreement (SLA) where the minimum acceptable performance level for system availability is specified by both parties.
The principle of availability does not address system functionality and usability. However, it does involve security-related criteria that may affect availability. Monitoring network performance and availability, site failover and security incident handling are critical.
Processing integrity clarifies whether a system delivers the right data at the right price at the right time. To ensure processing integrity, data processing must be complete, value, accurate, timely and authorized.
However, processing integrity does not necessarily imply data integrity. If data contains errors prior to being ingested into the system, detecting them may not be the responsibility of the processing entity. Monitoring of data processing, coupled with quality assurance procedures can help ensure processing integrity.
Data is considered confidential if its access and disclosure is restricted to a specified set of persons and organizations. Examples may include data intended only for company personnel, HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), business plans, intellectual property, internal price lists and other types of sensitive information.
Encryption is an important control for protecting confidentiality while data is in motion. Network and application firewalls, together with rigorous access controls, can be used to safeguard information being processed or stored on computer systems.
The privacy principle addresses the system’s collection, use, retention, disclosure, and disposal of personal information, should conform to the organization’s privacy notice, as well as with criteria set forth in the AICPA’s Generally Accepted Privacy Principles (GAAP). Personal identifiable information (PII) refers to details that can distinguish an individual such as name, address, Social Security number, etc. Some personal data related to health, race, sexuality, and religion is also considered sensitive and requires and extra level of protection under HIPAA. Controls must be put in place to protect all PII from unauthorized access.
Security
The Security principle refers to protection system resources against unauthorised accesss. Access controls help prevent potential system abuse, theft or unauthorized removal of data, misuse of software and improper alteration or disclosure of information. IT security tools such as network and web application firewalls or WAFs, two factor authentication and intrusion detection are useful in preventing security breaches that can lead to unauthorized access of systems and data.


Availability
The principle of availability refers to the accessibility of the system, its products, or services, as stipulated by a contract or service level agreement (SLA) where the minimum acceptable performance level for system availability is specified by both parties.
The Principle of availability does not address system functionality and usability. However, it does involve security-related criteria that may affect availability. Monitoring network performance and availability, site failover and security incident handling are critical.
Process Integrity
Processing integrity clarifies whether a system delivers the right data at the right time. To ensure processing integrity, data processing must be complete, value, accurate, timely and authorized.
However, processing integrity does not necessarily imply data integrity, if data contains errors prior to being ingested into the system, detecting them may not be the responsibility of the processing entity. Monitoring of data processing, coupled with quality assurance procedures can help ensure processing integrity.


Confidentiality
Data is considered confidential if its access and disclosure is restricted to a specified set of persons and organizations. Examples may include data intended only for company personnel, HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), business plans, intellectual property, internal price lists and other types of sensitive information.
Encryption is an important control for protecting confidentiality while data is in motion. Network and application firewalls, together with rigorous access controls, can be used to safeguard information being processed or stored on computer systems.
Privacy
The Privacy Principle addresses the system’s collection, use, retention, disclosure, and disposal of personal information, should conform to the organization’s privacy notice, as well as with criteria set forth in the AICPA’s Generally Accepted Privacy Principles (GAAP). Personal indentifiable information (PII) refers to details that can distinguish an individual such as name, address, Social Security number, etc. Some personal data related to health, race, sexuality, and religion is also considered sensitive and requires and extra level of protection under HIPAA. Controls must be put in place to protect all PII from unauthorized access.

Schedule a Security Review with us
+1 888 794.2266